Triangulating Mixed Methods Data
The goal of triangulation is to establish validity of the study findings by comparing the findings from the qualitative and quantitative data. This method of analysis is primarily used in concurrent mixed methods designs where the qualitative and quantitative data are obtained within the same time period, usually from the same sample. The process of triangulation begins with the researcher designing the study in which the same research question is examined using two different (qualitative and quantitative) methodologies.
These qualitative and quantitative data are then independently analyzed using traditional quantitative and qualitative data analysis methods to obtain two independent sets of results. The findings from both sets of data are then compared to determine if they have reached the same conclusions.
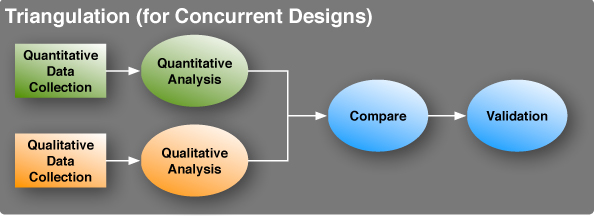
If it is found that the same conclusions are reached using both methods, this supports the veracity of the conclusions. If there is disagreement in the conclusions, this requires a further examination to reconcile the reasons why the two sets of data disagree. For example, such disagreement might suggest the need to analyze why the results are different for different subgroups within the sample (age, socioeconomic status, race, etc).
The next two pages suggest ways in which such group differences may be examined.
